Abstract
Objective In temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE), although hippocampal atrophy lateralizes the focus, the value of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to predict postsurgical outcome is rather modest. Prediction solely based on the hippocampus may be hampered by widespread mesiotemporal structural damage shown by advanced imaging. Increasingly complex and high-dimensional representation of MRI metrics motivates a shift to machine learning to establish objective, data-driven criteria for pathogenic processes and prognosis.
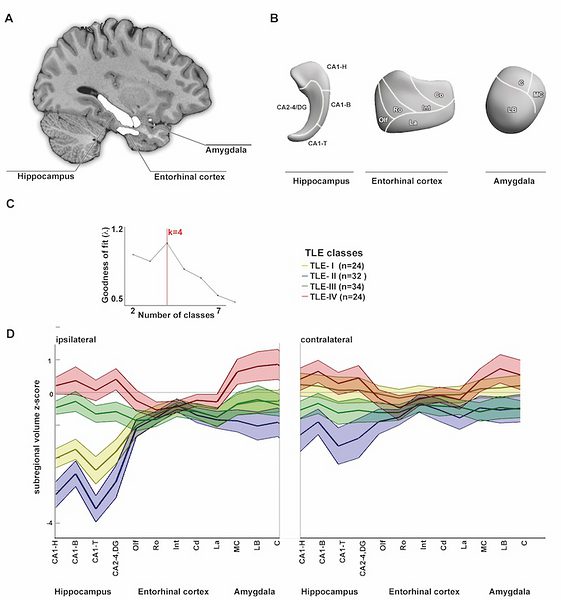
Methods We applied clustering to 114 consecutive unilateral TLE patients using 1.5T MRI profiles derived from surface morphology of hippocampus, amygdala, and entorhinal cortex. To evaluate the diagnostic validity of the classification, we assessed its yield to predict outcome in 79 surgically treated patients. Reproducibility of outcome prediction was assessed in an independent cohort of 27 patients evaluated on 3.0T MRI.
Results Four similarly sized classes partitioned our cohort; in all, alterations spanned over the 3 mesiotemporal structures. Compared to 46 controls, TLE-I showed marked bilateral atrophy; in TLE-II atrophy was ipsilateral; TLE-III showed mild bilateral atrophy; whereas TLE-IV showed hypertrophy. Classes differed with regard to histopathology and freedom from seizures. Classwise surface-based classifiers accurately predicted outcome in 92 ± 1% of patients, outperforming conventional volumetry. Predictors of relapse were distributed bilaterally across structures. Prediction accuracy was similarly high in the independent cohort (96%), supporting generalizability.
Interpretation We provide a novel description of individual variability across the TLE spectrum. Class membership was associated with distinct patterns of damage and outcome predictors that did not spatially overlap, emphasizing the ability of machine learning to disentangle the differential contribution of morphology to patient phenotypes, ultimately refining the prognosis of epilepsy surgery.