Abstract
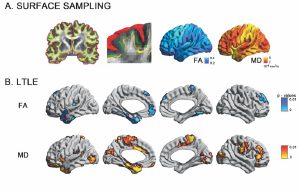
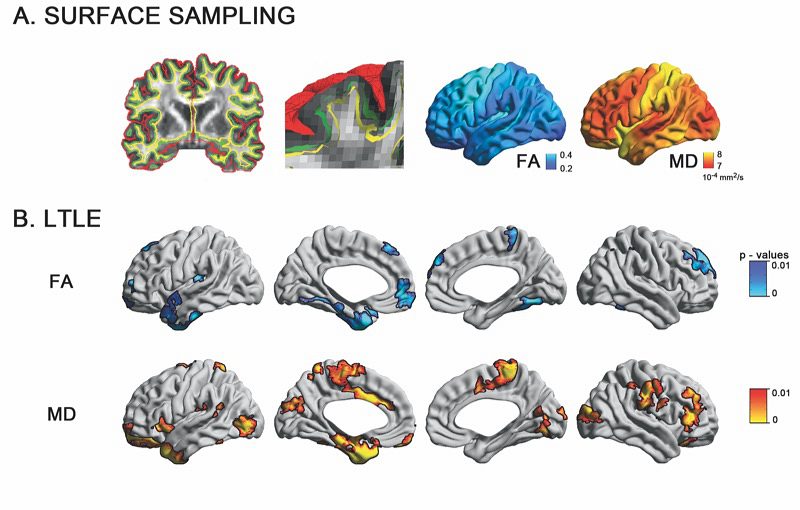
Drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy is increasingly recognized as a system-level disorder affecting the structure and function of large-scale grey matter networks. While diffusion magnetic resonance imaging studies have demonstrated deep fibre tract alterations, the superficial white matter immediately below the cortex has so far been neglected despite its proximity to neocortical regions and key role in maintaining cortico-cortical connectivity. Using multi-modal 3 T magnetic resonance imaging, we mapped the topography of superficial white matter diffusion alterations in 61 consecutive temporal lobe epilepsy patients relative to 38 healthy controls and studied the relationship to large-scale structural as well as functional networks. Our approach continuously sampled mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy along surfaces running 2 mm below the cortex. Multivariate statistics mapped superficial white matter diffusion anomalies in patients relative to controls, while correlation and mediation analyses evaluated their relationship to structural (cortical thickness, mesiotemporal volumetry) and functional parameters (resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging amplitude) and clinical variables. Patients presented with overlapping anomalies in mean diffusivity and anisotropy, particularly in ipsilateral temporo-limbic regions. Diffusion anomalies did not relate to cortical thinning; conversely, they mediated large-scale functional amplitude decreases in patients relative to controls in default mode hub regions (i.e. anterior and posterior midline regions, lateral temporo-parietal cortices), and were themselves mediated by hippocampal atrophy. With respect to clinical variables, we observed more marked diffusion anomalies in patients with a history of febrile convulsions and those with longer disease duration. Similarly, more marked diffusion alterations were associated with seizure-free outcome. Bootstrap analyses indicated high reproducibility of our findings, suggesting generalizability. The temporo-limbic distribution of superficial white matter anomalies, together with the mediation-level findings, suggests that this so far neglected region serves a key link between the hippocampal atrophy and large-scale default mode network alterations in temporal lobe epilepsy.